Over the last over a decade, we have undertaken a number of innovation and research projects to enhance our understanding of various identified topics, to provide innovative solutions as well as to expand our technical capabilities.

This is an extensive 4-year research program, investigating the feasibility of monitoring Antarctic ice cracking and calving events based on CTBTO hydroacoustic stations deployed in the Indian Ocean. The project involves long-range low-frequency sound propagation modelling prediction, multi-year large-scale hydroacoustic monitoring data processing and analysis, hydroacoustic source spectra frequency dispersion experimental and theoretical investigation, as well as temporal and spatial analysis of hydroacoustic event distributions.
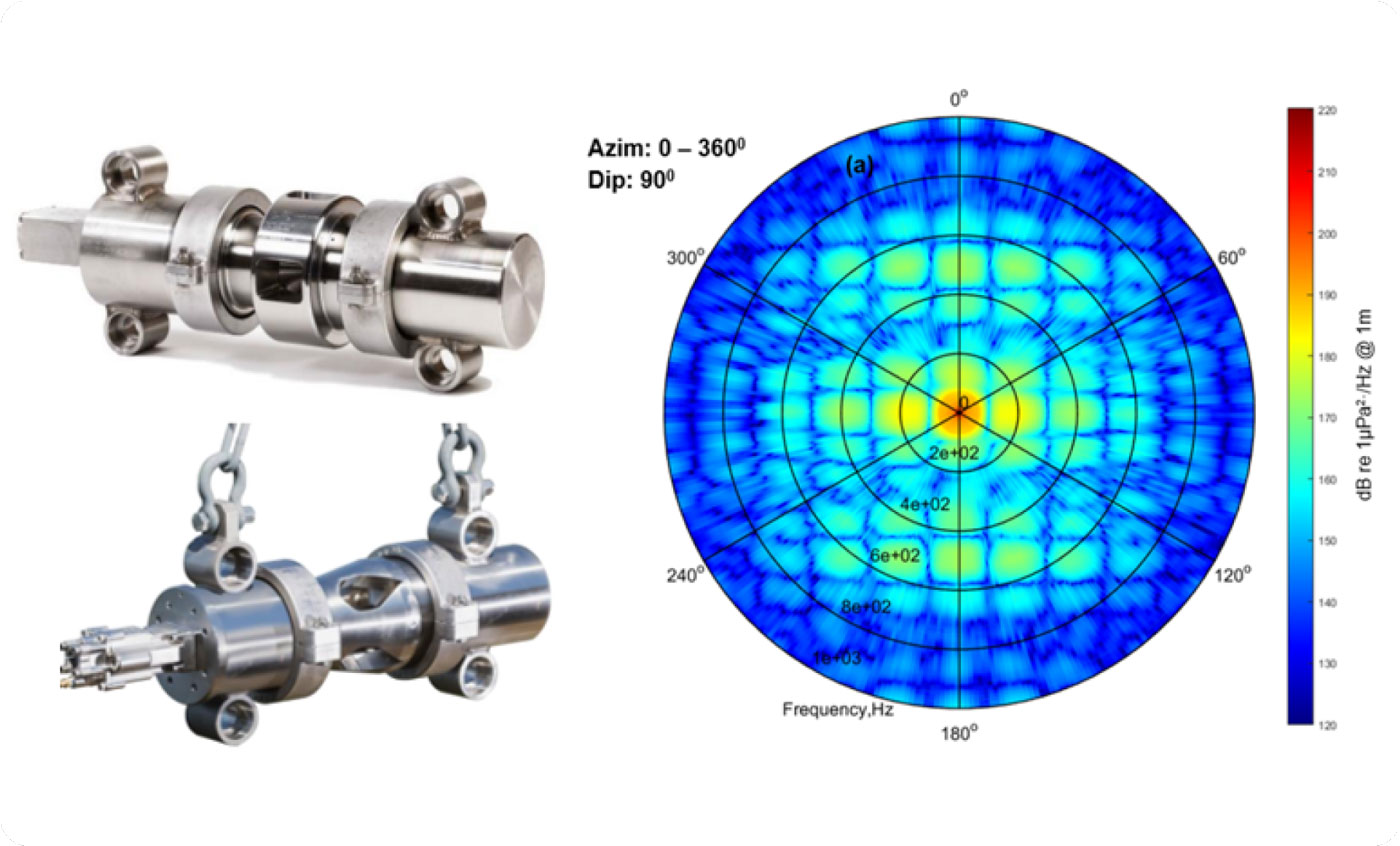
This noise emission numerical simulation is based upon the fundamental physics of the oscillation and acoustic radiation of source bubbles, and for an array source case, taking into account non-linear pressure interaction between source elements. The outputs of the numerical simulation include a set of ‘notional’ signature for each of the array elements, the far-field signature of the array source, its overall level directivity, and the source beam pattern / source spectra (linear, octave or 1/3 octave) at any direction.

This study undertakes a review of the classic theory of plane-wave reflection from layered solid media, and its application on revealing the mechanisms of the reflection loss from the seafloor with a specific geo-acoustic structure consisting of a sediment layer of weak elasticity overlaying a solid substrate. The significant reflection loss mechanisms include the compressional-shear wave conversion, the possible sediment-substrate surface wave excitation, and the resonances in the sediment layer.

The propagation and attenuation characteristics of railway generated vibration within Perth, WA is unique to other Australian states and territories given that predominant superficial ground conditions for the central metropolitan region are layered sandy soils. This study investigates the empirical prediction methodologies for rail-induced ground-borne vibration within sandy soils, for both at grade and underground cases, based on analyzing vibration measurements carried out for the passenger rail operations at multiple sites around central Perth metropolitan region.
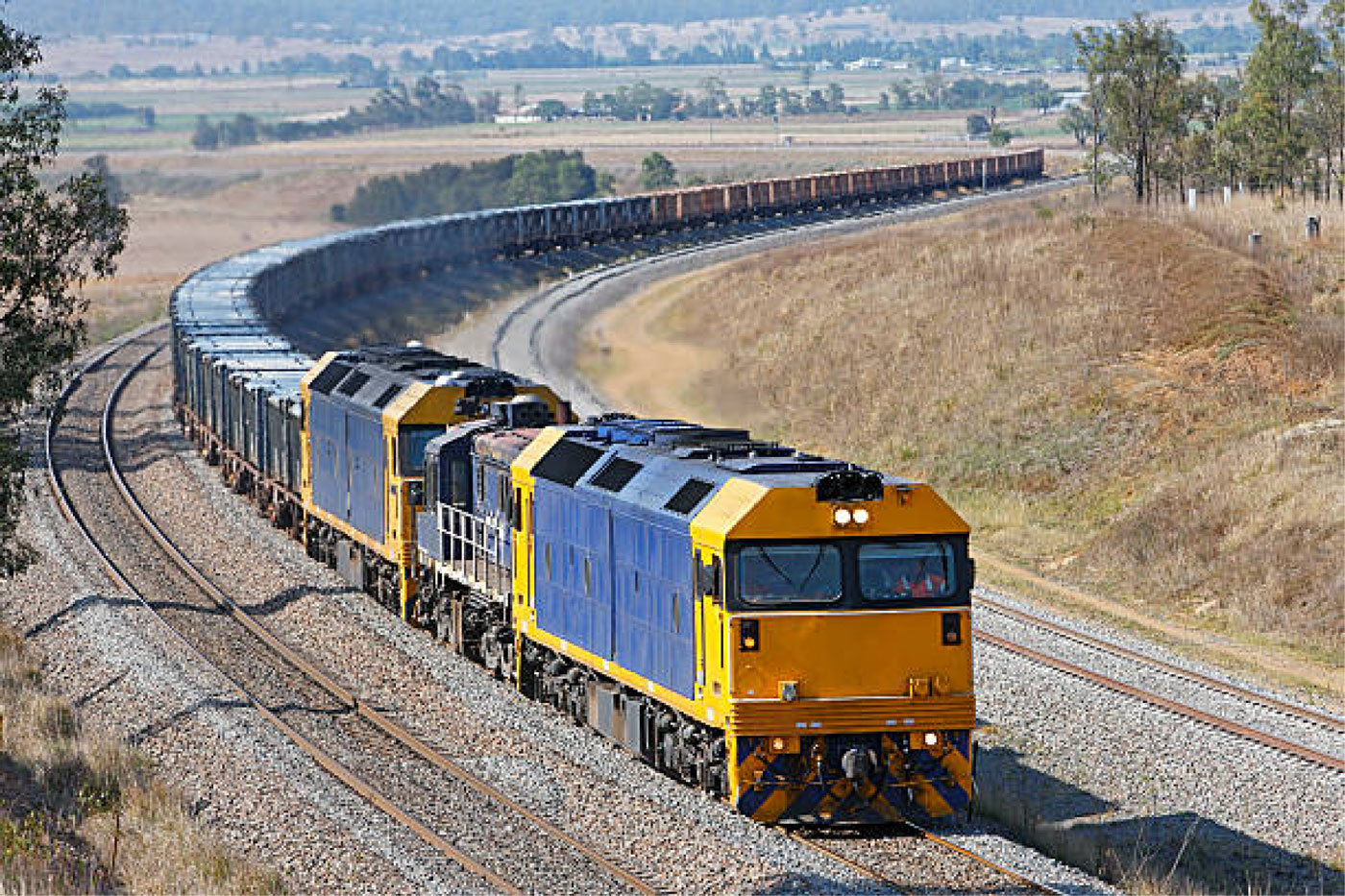

Curving noise from freight rail movements in the Perth metropolitan area have been investigated using Wayside Noise Monitoring System (WNMS) at a test location with an approximately 400-m radius rail curve section. The trackside noise, rail vibration and wheelset position and steering angle as measured by the WNMS kit have been analysed in detail. This study found that on the basis of monitoring data being consistent with previous research elsewhere, the principal mechanisms of curving noise at the test location are most likely steering-controlled.

Pressure pulsation, created by the operation of hydraulic pumps in a fluid power system, is one of the primary causes of noise issues from hydraulic machinery. The wave energy resulting from such pulsation propagates in both the wall and the fluid of the flow pipes associated with the fluid power systems, inducing fluid-borne vibration of the pipes and the consequent noise radiated from the pipes. This study presents noise and vibration measurements for a series of marine hydraulic mooring winch systems installed on a marine barge (Transhipper), and proposes the installation of passive pulsation suppressors as the most practical solution to control pulsation from the fluid power units and the consequent excessive noise radiation from the flow pipes.